Some Examples Of Homologous Structures: A Comprehensive Guide
Homologous structures are fascinating examples of evolutionary biology that reveal the shared ancestry of diverse species. These structures provide compelling evidence of how organisms have evolved from common ancestors, adapting to their environments while retaining similar underlying anatomical features. By understanding homologous structures, we gain insight into the intricate processes of evolution and the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
In this article, we will explore the concept of homologous structures in detail, delving into examples from various organisms and discussing their significance in the field of biology. Whether you're a student, educator, or simply curious about the wonders of nature, this article will provide a thorough understanding of homologous structures and their importance in evolutionary studies.
From the wings of birds to the flippers of dolphins, homologous structures demonstrate how similar anatomical features can serve vastly different functions. By examining these structures, scientists can trace the evolutionary pathways that have shaped the diversity of life. Let's dive deeper into the world of homologous structures and uncover their secrets.
Read also:Daily Courier Prescott Obituaries A Comprehensive Guide To Honoring Lives
Table of Contents
- What Are Homologous Structures?
- Examples of Homologous Structures
- Homologous Structures in Vertebrates
- Homologous Structures in Plants
- Distinguishing Homologous from Analogous Structures
- Evolutionary Significance
- Molecular Basis of Homology
- Fossil Evidence
- Misconceptions About Homologous Structures
- Conclusion
What Are Homologous Structures?
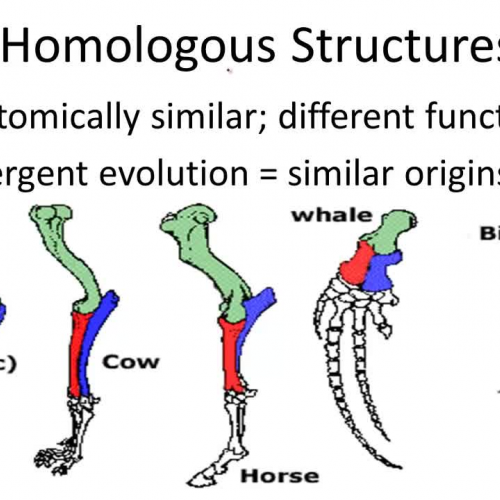
Homologous structures refer to anatomical features in different species that share a common ancestry. These structures may have different functions but exhibit similar underlying characteristics due to their evolutionary origins. For example, the forelimbs of humans, bats, and whales are homologous structures, as they share a common ancestor despite serving different purposes.
The concept of homology is fundamental to the study of evolution and helps scientists understand how species have adapted to their environments over time. By comparing homologous structures, researchers can reconstruct evolutionary relationships and identify patterns of descent.
Examples of Homologous Structures
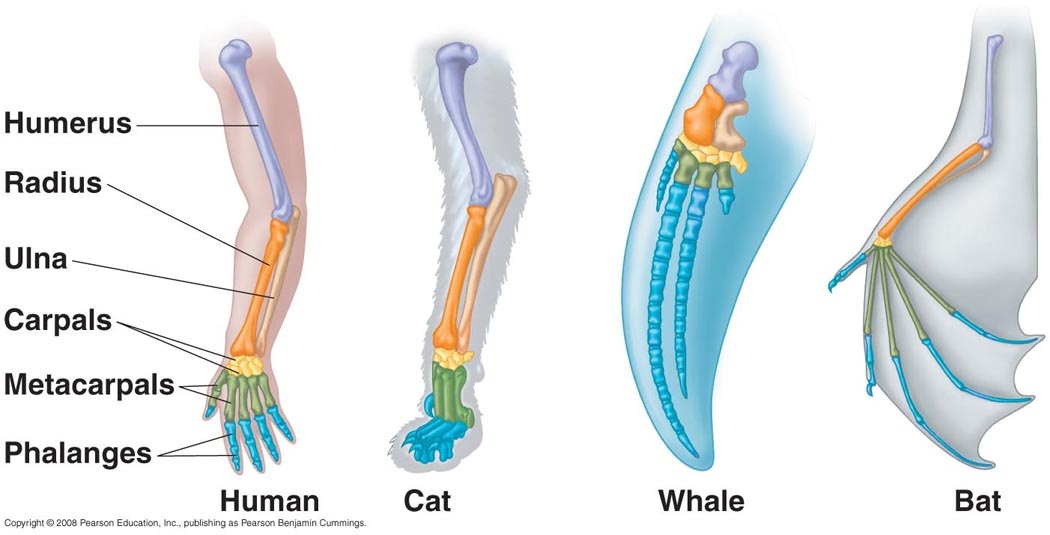
Forelimbs in Mammals
One of the most commonly cited examples of homologous structures is the forelimbs of mammals. Despite their varied functions, the forelimbs of humans, cats, whales, and bats share a similar bone structure, including the humerus, radius, and ulna. This similarity indicates a shared evolutionary origin, even though these animals use their forelimbs for walking, flying, swimming, or grasping.
Wings in Birds and Bats
Although both birds and bats have wings, their wings are homologous structures rather than analogous ones. Both structures evolved from the forelimbs of a common ancestor, but they serve similar functions of flight. This example highlights how homologous structures can evolve to perform similar roles in different species.
Homologous Structures in Vertebrates
Vertebrates provide numerous examples of homologous structures that demonstrate the principles of evolution. The skeletal systems of fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals share many similarities, reflecting their shared ancestry. For instance:
- Vertebral columns in all vertebrates exhibit a similar arrangement of bones.
- The jawbones of fish and mammals share a common origin, despite their different functions.
- Limbs in tetrapods (four-legged animals) exhibit a consistent pattern of bones, including the humerus, radius, and ulna.
Homologous Structures in Plants
Plants also exhibit homologous structures, such as leaves, stems, and roots. For example:
Read also:Caballero Rivero Woodlawn Cemetery A Legacy Of Elegance And Serenity In Miami Fl
- Leaves in different plant species may vary in shape and function but share a common evolutionary origin.
- Stems in trees and herbaceous plants exhibit similar vascular structures, indicating a shared ancestry.
- Root systems in various plants show homologous features, such as the arrangement of xylem and phloem tissues.
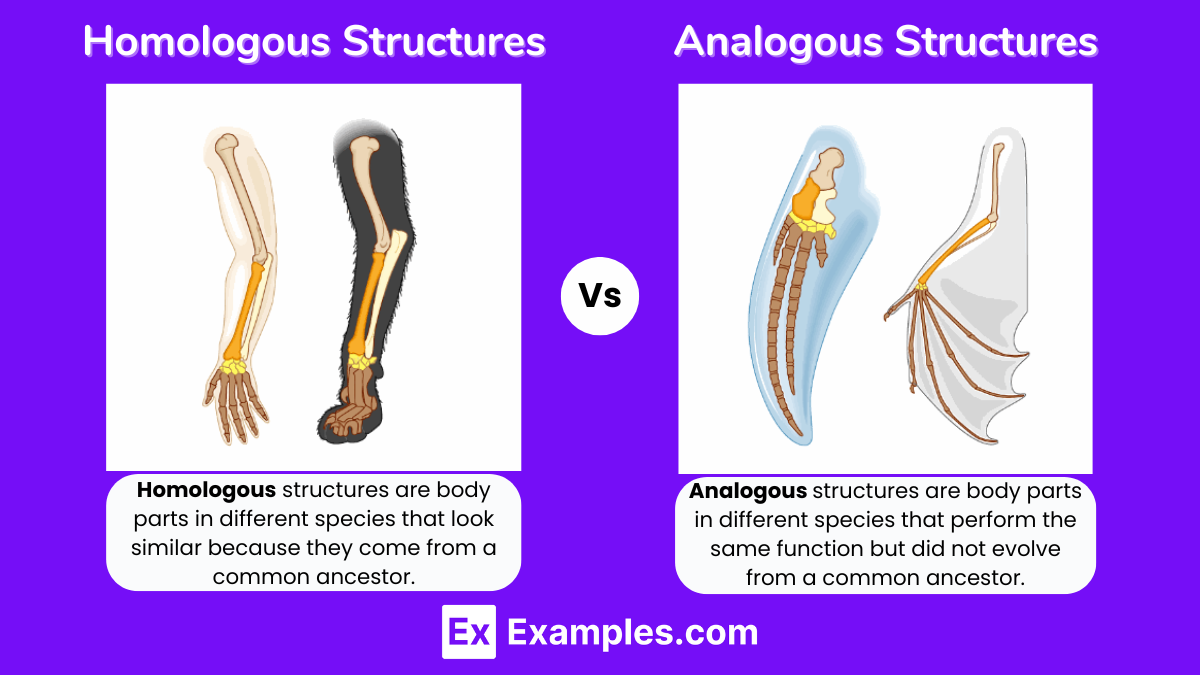
Distinguishing Homologous from Analogous Structures
It is essential to differentiate between homologous and analogous structures, as they represent different evolutionary processes. While homologous structures share a common ancestry, analogous structures have evolved independently to serve similar functions. For example:
- The wings of birds and insects are analogous structures, as they evolved separately to enable flight.
- The eyes of humans and octopuses are analogous structures, as they serve the same purpose but have different evolutionary origins.
Evolutionary Significance
Homologous structures provide crucial evidence for the theory of evolution. By studying these structures, scientists can trace the evolutionary history of species and identify patterns of descent. The presence of homologous structures across diverse organisms supports the idea that all life shares a common origin and has evolved through natural selection and genetic mutation.
Molecular Basis of Homology
Advances in molecular biology have revealed the genetic basis of homologous structures. Many homologous structures are controlled by similar genes and developmental pathways, even in distantly related species. For example:
- The Hox genes, which regulate limb development, are conserved across a wide range of organisms, from fruit flies to humans.
- Conserved genetic sequences in plants and animals demonstrate the shared ancestry of homologous structures at the molecular level.
Fossil Evidence
Fossils provide valuable evidence of homologous structures and their evolutionary history. Transitional fossils, such as Archaeopteryx, demonstrate the gradual development of features like wings and feathers in birds. By studying fossil records, scientists can reconstruct the evolutionary pathways that led to the diversity of life on Earth.
Misconceptions About Homologous Structures
There are several common misconceptions about homologous structures that can lead to misunderstandings about evolution. For example:
- Homologous structures do not necessarily imply identical functions; they simply share a common ancestry.
- Not all similar structures are homologous; some may be analogous or convergent.
Conclusion
Homologous structures are a testament to the power of evolution and the interconnectedness of life on Earth. By examining these structures, we gain insight into the processes that have shaped the diversity of species and the mechanisms that drive adaptation. This article has explored various examples of homologous structures, their significance in evolutionary biology, and the importance of distinguishing them from analogous structures.
We encourage you to leave a comment or share this article with others who are interested in the fascinating world of evolutionary biology. For further reading, explore our other articles on topics such as natural selection, genetic drift, and the history of life on Earth. Together, we can deepen our understanding of the natural world and the incredible processes that have shaped it.
Data sources and references:
- Darwin, C. (1859). On the Origin of Species.
- Carroll, S. B. (2006). Endless Forms Most Beautiful: The New Science of Evo Devo.
- University of California Museum of Paleontology. Understanding Evolution.