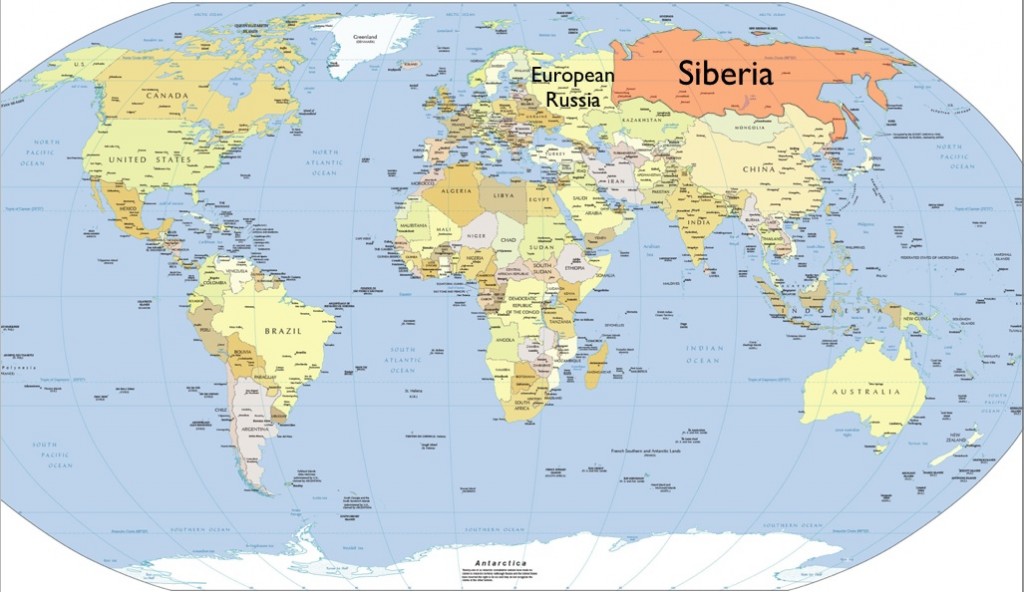
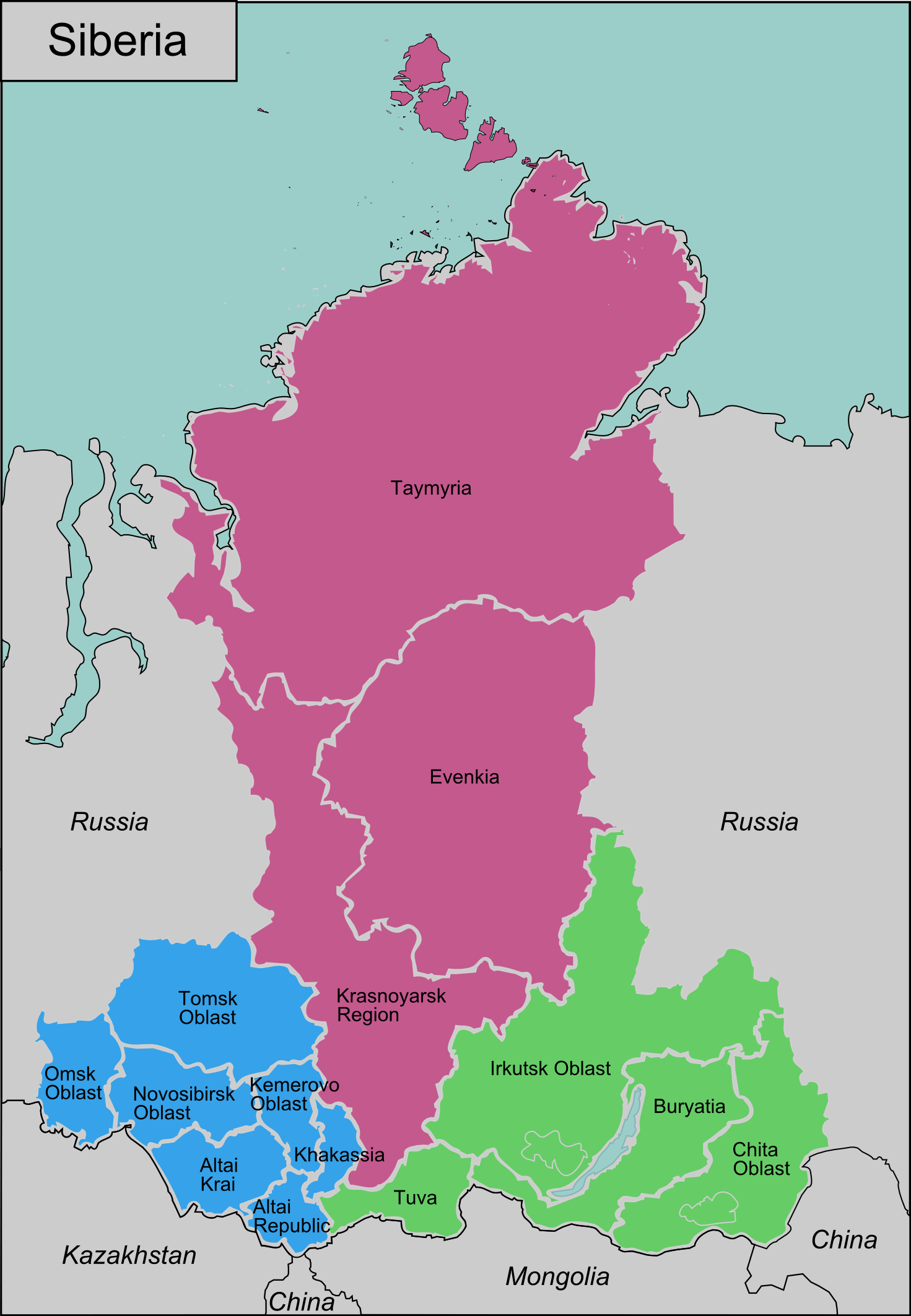
Siberia Location: Discovering The Vast And Enigmatic Region
Siberia location is a topic that has intrigued geographers, explorers, and history enthusiasts for centuries. Covering an expansive area in Northern Asia, Siberia is a land of extremes, from its breathtaking natural beauty to its harsh climate conditions. This region, which constitutes a significant part of Russia, plays a crucial role in global geopolitics, economics, and environmental studies.
Siberia is not just a remote and mysterious land; it is a vital piece of the global puzzle. Its rich history, diverse ecosystems, and abundant natural resources make it a fascinating subject of study. From the early days of exploration to the modern era of industrial development, Siberia has evolved into a region of immense importance.
In this article, we will delve into the geographical, historical, and cultural aspects of Siberia. Whether you're a student, a traveler, or simply a curious reader, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the Siberia location and its significance in today's world.
Read also:Hanes Lineberry Funeral Home Sedgefield Chapel A Compassionate Legacy In Funeral Services
Table of Contents
- Geographical Overview of Siberia
- History of Siberia
- Climate Conditions in Siberia
- Natural Resources of Siberia
- Ecosystems and Biodiversity
- Population and Demographics
- Transportation and Infrastructure
- Economy of Siberia
- Tourism in Siberia
- Future Prospects and Challenges
Geographical Overview of Siberia
Siberia, located in the northern part of Asia, is an expansive region that stretches from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. Covering approximately 13.1 million square kilometers, it constitutes about 77% of Russia's total land area.
Boundaries and Landmarks
The geographical boundaries of Siberia include the Ural Mountains to the west, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the east. Key landmarks such as the Lena River, Yenisei River, and Lake Baikal further define this vast territory. Lake Baikal, the world's deepest freshwater lake, is a notable feature of the Siberia location.
Regions within Siberia
- Western Siberia: Known for its vast plains and rich oil reserves.
- Central Siberia: Characterized by mountain ranges and dense forests.
- Eastern Siberia: Home to Lake Baikal and the Pacific coastline.
Siberia's diverse landscapes range from frozen tundras to lush taiga forests, making it one of the most ecologically diverse regions in the world.
History of Siberia
The history of Siberia dates back thousands of years, with evidence of early human settlements found in the region. Over time, Siberia has been shaped by various cultural influences and political changes.
Early Settlements
Ancient tribes such as the Scythians and the Turkic peoples were among the first to inhabit the Siberia location. These early settlers relied on hunting, fishing, and nomadic herding for survival.
Russian Exploration
The Russian exploration of Siberia began in the 16th century under the leadership of Cossack adventurers. By the 17th century, Russia had established control over much of the region, leading to significant cultural and economic exchanges.
Read also:Council Bluffs Death Notices A Comprehensive Guide To Remembering And Honoring The Departed
Climate Conditions in Siberia
Siberia is renowned for its extreme climate, which varies significantly across its vast territory. The region experiences long, harsh winters and short, mild summers, making it one of the coldest inhabited places on Earth.
Temperature Extremes
Temperatures in Siberia can drop as low as -68°C (-89°F) in the winter and rise to around 30°C (86°F) in the summer. The coldest inhabited place on Earth, Oymyakon, is located in Siberia.
Seasonal Changes
- Winter: Lasting from October to April, characterized by snowfall and freezing temperatures.
- Summer: Brief and mild, with longer daylight hours due to the polar day phenomenon.
Understanding the climate conditions of Siberia is essential for anyone planning to visit or study the region.
Natural Resources of Siberia
Siberia is rich in natural resources, making it a key player in the global energy market. The region is home to vast reserves of oil, natural gas, and minerals.
Energy Resources
Siberia holds significant reserves of oil and natural gas, with major production centers located in Western Siberia. These resources contribute significantly to Russia's economy and global energy trade.
Mining and Minerals
- Gold: Siberia is one of the largest producers of gold in the world.
- Diamonds: The Mirny Mine in Eastern Siberia is one of the largest diamond mines globally.
- Coal: Abundant coal reserves are found in the Kuznetsk Basin.
These resources have played a crucial role in shaping Siberia's economic landscape.
Ecosystems and Biodiversity
Siberia's diverse ecosystems support a wide range of plant and animal species. From the taiga forests to the Arctic tundra, the region is home to unique biodiversity.
Taiga Forests
The taiga, or boreal forest, is the largest terrestrial biome in the world, covering much of Siberia. It is home to species such as the Siberian tiger, brown bear, and numerous bird species.
Arctic Tundra
The Arctic tundra, located in the northern part of Siberia, is characterized by permafrost and sparse vegetation. This ecosystem supports species like the Arctic fox, reindeer, and various migratory birds.
Population and Demographics
The population of Siberia is relatively sparse compared to its vast land area. However, the region is home to a diverse mix of ethnic groups and cultures.
Ethnic Diversity
Siberia's population includes indigenous groups such as the Yakuts, Tuvans, and Evenks, as well as Russian settlers and other ethnic minorities. Each group contributes to the rich cultural tapestry of the region.
Urbanization
Major cities in Siberia, such as Novosibirsk, Omsk, and Irkutsk, serve as economic and cultural hubs. These cities have experienced significant growth and development over the years.
Transportation and Infrastructure
Transportation in Siberia is challenging due to its vast distances and harsh climate. However, the region has developed a robust infrastructure to support its economic activities.
Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway is one of the most famous transportation networks in the world, connecting Moscow to Vladivostok. It plays a crucial role in the movement of goods and people across Siberia.
Road and Air Networks
- Roads: Major highways connect key cities, although road conditions can be challenging in remote areas.
- Airports: Several international and domestic airports serve Siberia, facilitating travel and trade.
Improving transportation infrastructure remains a priority for the region's development.
Economy of Siberia
Siberia's economy is driven by its natural resources, industrial activities, and growing service sectors. The region's contribution to Russia's GDP is significant, making it a vital economic hub.
Industrial Sectors
The primary industries in Siberia include energy, mining, manufacturing, and agriculture. These sectors provide employment opportunities and drive economic growth.
Trade and Investment
Siberia's strategic location makes it an important player in international trade. The region attracts significant foreign investment, particularly in the energy and mining sectors.
Tourism in Siberia
Siberia offers a unique blend of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and adventure tourism opportunities. From exploring Lake Baikal to skiing in the Altai Mountains, the region has much to offer visitors.
Popular Tourist Destinations
- Lake Baikal: Known for its crystal-clear waters and stunning landscapes.
- Altai Mountains: Perfect for hiking, skiing, and nature lovers.
- Novosibirsk: The cultural and scientific center of Siberia.
Tourism in Siberia continues to grow, attracting both domestic and international travelers.
Future Prospects and Challenges
The future of Siberia is shaped by its potential for growth and the challenges it faces in terms of environmental sustainability and economic development.
Environmental Concerns
Climate change poses a significant threat to Siberia's ecosystems and permafrost regions. Efforts are underway to mitigate the impact of global warming on the region.
Economic Development
Investment in infrastructure, technology, and education will be crucial for Siberia's future growth. The region has the potential to become a leading player in the global economy.
Conclusion
Siberia location is a region of immense significance, offering a wealth of natural resources, cultural heritage, and economic opportunities. From its extreme climate to its diverse ecosystems, Siberia continues to captivate the imagination of people around the world.
We encourage readers to explore further and share their thoughts in the comments section. For more insights into global geography and culture, be sure to check out our other articles. Together, let's continue to discover the wonders of our world!